I:What is Flash
- Macromedia Flash is an animation program that uses vectors to created images and animations. The computer interpolates these vectors as mathematical algorithms which results in the creation of relatively small files.
- Flash provides a full-fledged scripting language called ActionScript for adding actions in order to control the Flash movies.
- Flash has become a popular program for creating animations and Web sites for the Internet.
- Some of the advantages of using Flash:
- Flash provides an efficient way to deliver images and animations over the Web.
- Vector images are scaleable, which means that you can control what a Web site looks like when your viewer resizes the browser window.
- Flash provides streaming ability, which means that the user does not have to wait for the information to completely download before view it. As Flash plays the first frames of your movie, subsequent frames keep downloading and are fed at a specific rate so that the viewer sees only a continuous flow of images.
- Flash animations can also include navigational buttons and menus.
- The Flash Player can be licensed and Flash movies can be distributed on CD-ROM.
- Flash movies can be exported as stand-alone projectors and distributed via email or on a disk.
- Flash movies can be exported to other formats, such as QuickTime or Windows AVI files.
II: Two Types of Computer Images
- Raster Based images.
- These images are made up of pixels.
- A pixel is a term for "picture element". These are the smallest unit of color that can be seen on a monitor. Below are two versions of the same image - a red circle on a white background. The second version is highly magnified so that the pixels can be seen,
- Photographic images are a good example of raster based images.
- Software programs such as Photoshop convert image files to raster based images so that these images can be edited.
- Vector Based images.
- These images are really not images to a computer. A computer sees these images as mathematical algorithms.
- The two pumpkin images below are examples of vector images created in Flash. The first image is what appears on the screen. The second image (blue line )is what the computer works with to interpolate the algorithms.
- Because vector images are not really images the files are much smaller.
III: How Flash Animates
- Flash uses standard animation techniques to create the illusion of movement.
- A series of still images, each slightly different from the next are created. These images are called frames.
- By displaying the frames rapidly, one after the other, the illusion of continuous movement is created.
- Turning on the onion skinning button allows you to view the the individual frames simultaneously.
IV: Flash Movie Formats
- Flash is both an authoring environment for creating animations and a playback system for making the animations viewable on a local computer or a Web browser.
- Flash Files have two extensions. These are .fla and .swf.
- The animation and interactivity are created in the Flash authoring files. These files have the .fla extension.
- To view the files the .fla authoring files are converted to Flash Player format. These files have the .swf extension.
V: Objects, Shapes, Symbols and Instances
- Object: any graphic or text item on the stage or in a script.It can be a shape or a symbol or a bitmap image.
- Shape: an object that has been created in Flash and has not been converted to a symbol
- Symbol: Converting a shape to a symbol allows Flash to for a more efficeint way to calculate a symbol in the animation. This creates lless file size in most situations. Certain functions such as "tweening" and fading cannot be performed unless the shape is converted to a symbol.
- There are three types of symbols in Flash:
- Movie Clips; These are symbols that can be little movies within the main movie in Fash. Using ActionScript gives you the most controls over Mopvie Clip symbols. It is suggested that when in doubt convert your shape or image to a Movie Clip. The behavior of the symbol can be changed any time.
- Buttons; These symbols are used to control the Movie Clip symbols.
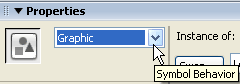
- Graphic: These symbols are used when an object is to remain inactive. A good example of a inactive symbol is a button on a Web page. If you are on the "home" page you do not want the "home" button to be active because clicking it will take you nowhere.
The button is converted to a graphic symbol by changing the behavior in the drop-down menu in the upper left corner of the of the Properties panel. The color can be changed to indicated that it is inactive.
- Instance: is a copy of a symbol. Each time a symbol is reused from the project file it is called an instance. The color, size , shape and position of an instance can be altered and can be different than the symbol.
Copyright © 2006, Christalene Loren. All rights Reserved.